
When sending an e-mail, the service from which the e-mail is sent may be unable to reach the destination address. When an e-mail arrives at the destination server for an address (such as mymail.example, when sending to it may be that the mail daemon is unable to deposit the message in the specified user's mailbox if the underlying hard drive of the server has insufficient space.īounce due to unreachable destination When a server accepts a message for delivery, it is also accepting the responsibility to deliver a bounce message in the event that delivery fails.īounce due to lack of disk space A sender may sometimes receive a bounce message from their own mail server, reporting that it has been unable to send a message, or alternatively from a recipient's mail server reporting that although it had accepted the message, it is unable to deliver it to the specified user.
Moreover, a temporary suspension of the recipient's email or a temporary error on the server are also causes of a soft bounce.Įrrors may occur at multiple places in mail delivery. Additional situations in which a soft bounce appears is a block set up on the recipient's email to mark a certain sender as a 'spam' sender, or to blacklist a certain sender.
#DELIVERY STATUS NOTIFICATION FAILURE OUTLOOK FULL#
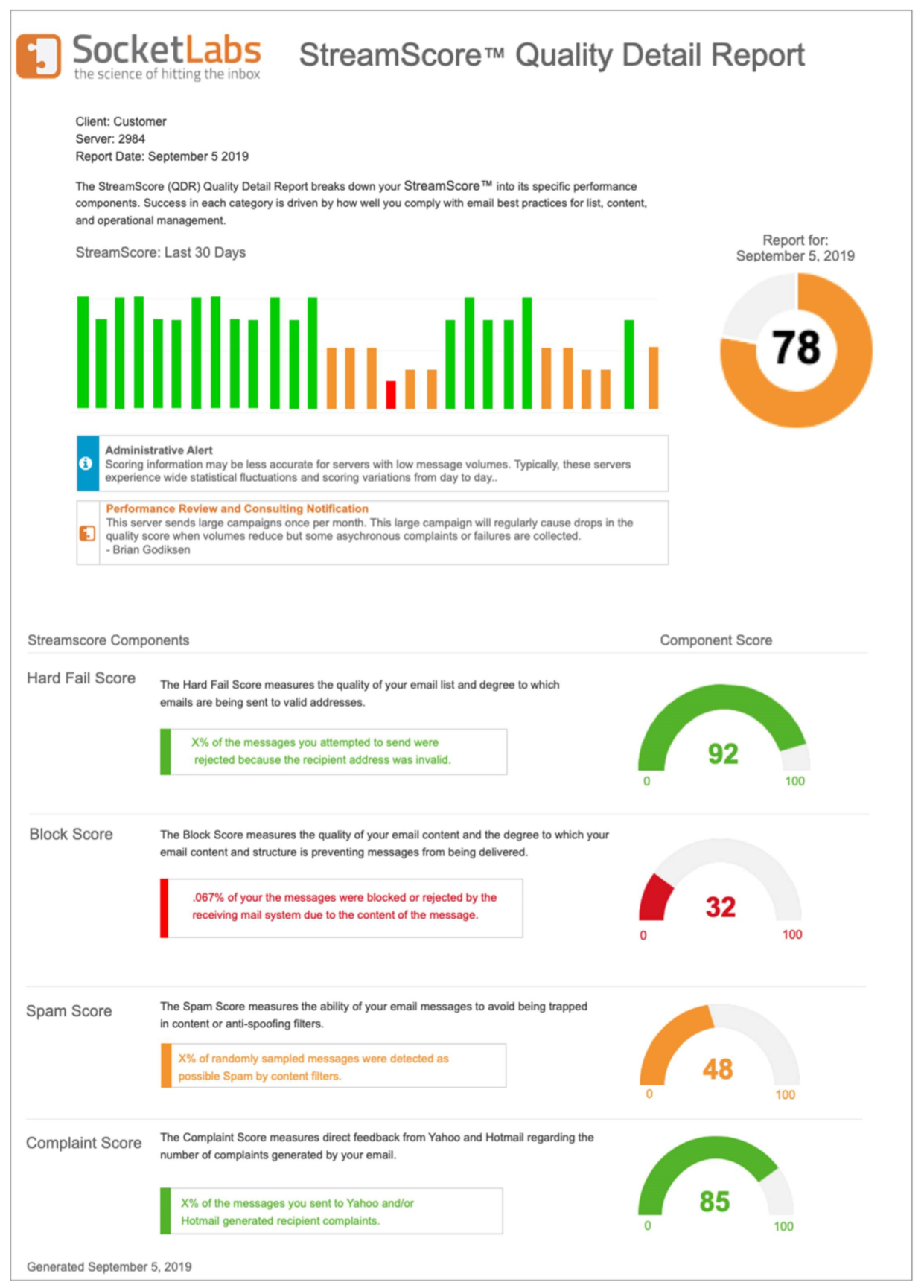
Soft bounces happen when the recipient of the email has either a full Inbox and therefore no space to store another email, or a limit on the size of the emails that it is allowed to receive. A bounced message that experiences a soft bounce may be tried to be redelivered at another time. In this case, removal of the email addresses that bounce back is mandatory. A few of the occasions when hard bounces occur are when the recipient of the email finds himself in one of the following situations: incorrect identifier/incorrect domain (such as a typo in the email address or in the domain) or his server does not accept emails anymore. Hard bounces occur when the sender's mail server determines that there is a high likelihood that the recipient is unavailable and is likely to remain so. Hard bounces are permanent and they score higher in terms of sender's IP damage. Briefly, the total bounce rate is calculated as the sum of the hard bounce rate and soft bounce rate. Both of them affect the IP reputation of the sender because the Email Service Providers (ESPs) consider the total bounce rate as a decision factor when directing the email into a user's Inbox. Therefore, two types of email bounces have been created: hard bounces and soft bounces. The email systems have been enhanced with reputation systems tied to the actual sender of the email, with the idea of recipient's email servers rejecting email when a forged sender is used in the protocol.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
